Nancy Grace Roman Telescope (Roman)
Roman is an infrared telescope named after Nancy Grace Roman (1925-2018) who was NASA’s first chief astronomer and is known as the ‘Mother of Hubble.’ Roman has two main objectives: discovering the cause of the expansion of the universe and searching for exoplanets. Roman and the James Webb Space Telescope offer broader ranges of sight than the Hubble Space Telescope and are steps NASA is taking to uncover the secrets of space. The Engineering and Technology Directorate at Goddard has made multiple contributions to the Roman Space Telescope such as the PRISM and GRISM, which are instruments used to pinpoint the speed and distance of stars and galaxies in relation to Earth.
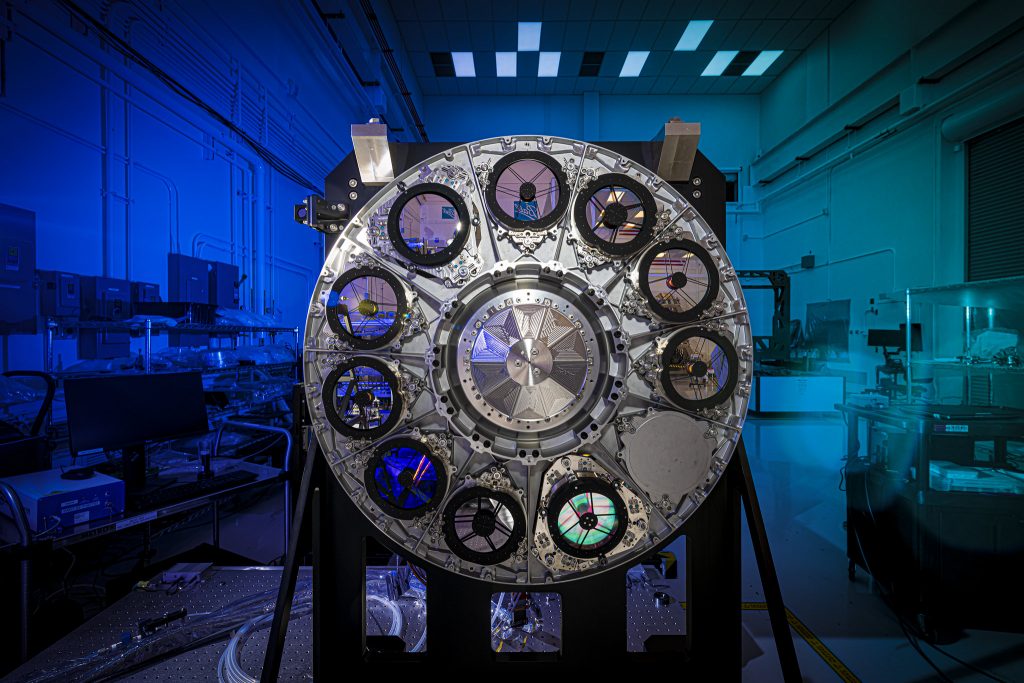
Engineers at Goddard designed, built and tested Roman’s Focal Plane System (FPS) which has been delivered to Ball Aerospace to be integrated into the Wide Field Instrument (WFI). The instrument, with its 18 detectors, allows the telescope to capture high-resolution images of the universe.
As such, the Nancy Grace Roman Space telescope looks to make advancements in the understanding of dark energy, exoplanets, astrophysics and various other scientific subdisciplines.
