Unlocking the Universe
Collaborative Multidisciplinary Engineering Across NASA and Partner Organizations
Expanding The World’s Engineering Boundaries
The Engineering and Technology Directorate (ETD) provides multidisciplinary engineering expertise for the development of cutting-edge Science and Exploration Systems and technologies. This talented workforce is committed to expanding today’s engineering boundaries through the application of emerging technologies to develop high-performance, cost-effective solutions to the most challenging problems in space exploration. The ETD achieves this within Goddard’s laboratories and those of the valued present and future partners.
Projects in Development
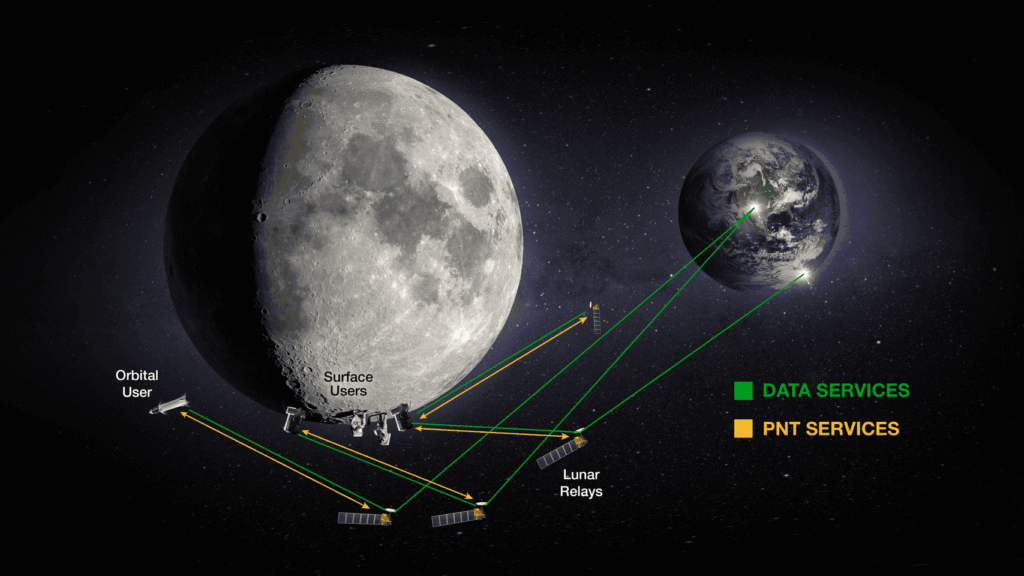
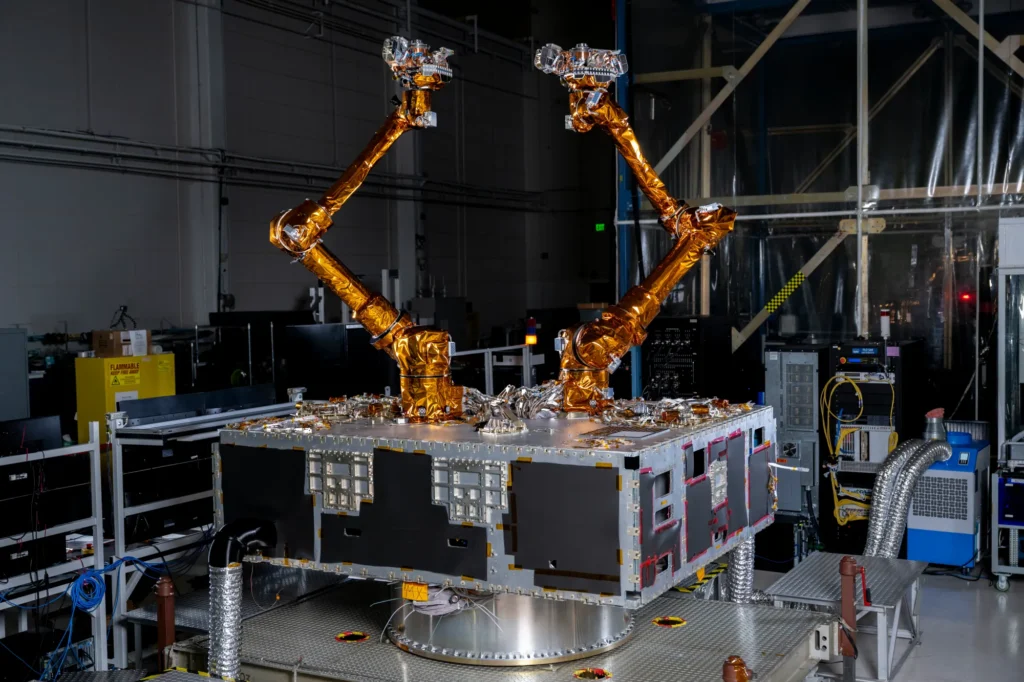
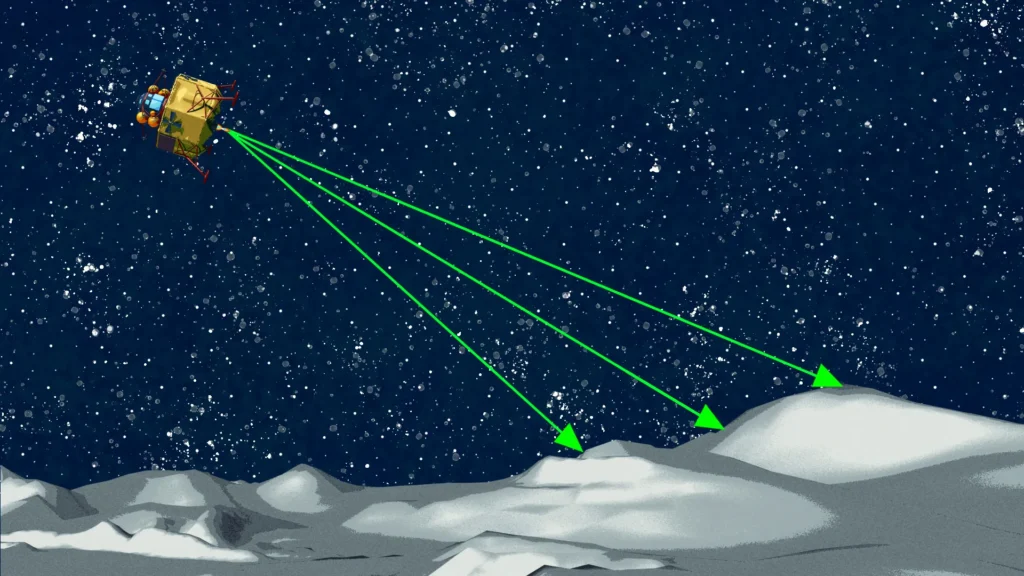
ETD has numerous active efforts supporting a wide range of missions and projects. This is a sampling of some of the ongoing technical efforts to design, build, or test spaceflight hardware to enable NASA’s mission of exploration and American technological leadership.
Projects in Operation and Historical Missions
ETD’s projects in operation and historical missions demonstrate decades of successful multidisciplinary engineering excellence. Our engineers ensure space situational awareness, safeguard assets and provide data to our stakeholders and decision makers.
New Technology and IRADs
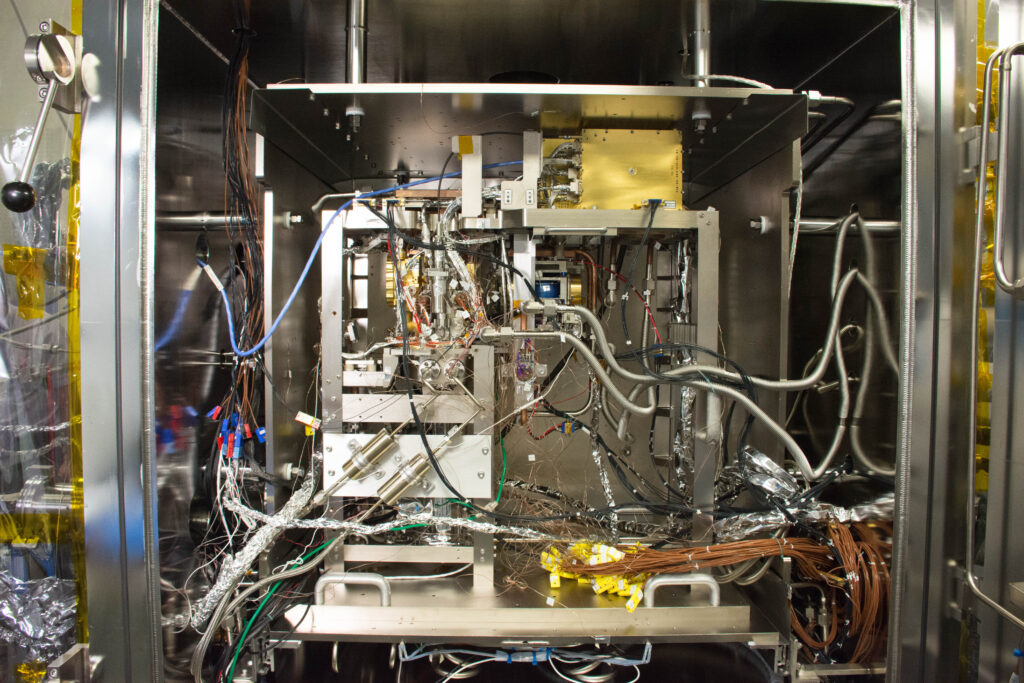
New technology projects and the Internal Research and Development (IRAD) program drive ETD’s innovation efforts by funding strategic risk-reduction activities, advanced concept development, and high-impact initiatives. Featuring both competitive selection and strategically directed initiatives, these efforts enable our engineering teams to develop cutting-edge technologies and innovative solutions for the most challenging problems in space exploration, advancing our capabilities for future missions.